
All You Need to Know
At Homerun, we believe high-purity silica sand to be a critical raw material for assisting in the worlds transition to clean energy. As the world shifts towards a greener, more sustainable future, the demand for silica sand is likely to increase drastically, making it a crucial resource in the global effort to combat climate change.
Find out why below:
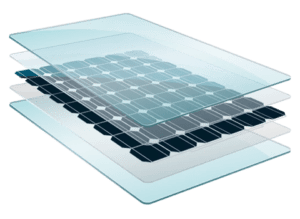





Our modern society is built on materials. HPQ Silica, is one of these materials, and is used in multiple industrial and commercial products including many solutions in the energy and technology sectors. In the manufacture of solar systems, HPQ Silica is the basic material used to produce both polysilicon and solar glass. In the manufacture of mobile devices, HPQ Silica is used to produce both processing chips and interactive glass. Without HPQ Silica, there would be no solar energy generation and there would be no mobile devices.
HPQ silica sand, also known as High Purity Quartz sand, is a specialized form of silica sand that is exceptionally pure and consists of high levels of quartz.
HPQ silica sand stands out due to its remarkable purity, with quartz content exceeding 99.99%. This high purity level makes it ideal for various high-tech applications.
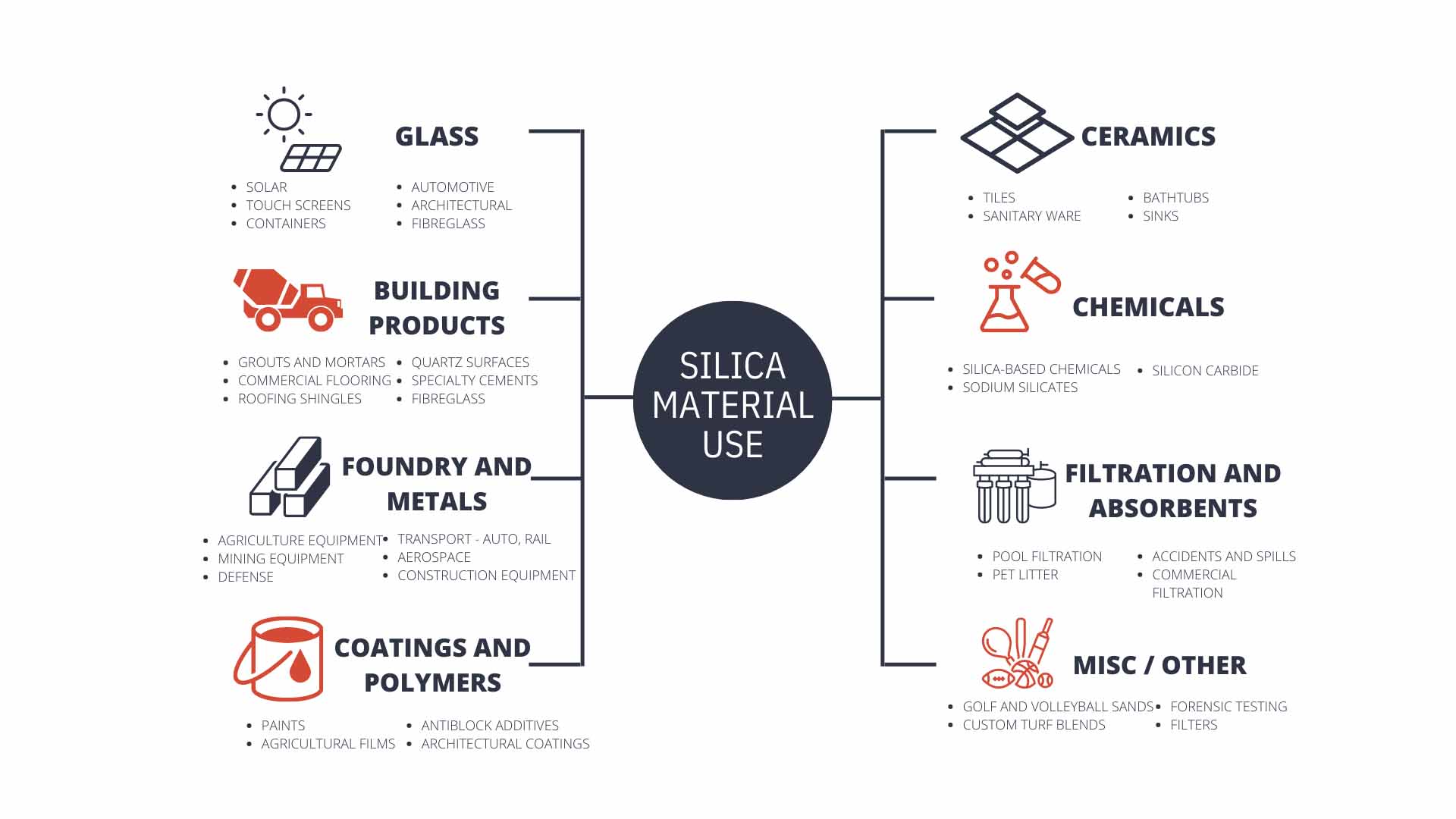
HPQ silica sand finds applications in industries such as electronics, optics, solar panels, and semiconductors due to its excellent properties, including high thermal and chemical resistance.
HPQ silica sand is typically extracted through conventional mining methods and then undergoes various processes like screening, washing, and flotation to remove impurities and achieve its high purity level.
High purity in HPQ silica sand is crucial because impurities can negatively impact the performance of products it’s used in. In industries like electronics, even minute impurities can cause defects.
While HPQ silica sand is more commonly associated with high-tech industries, its unique properties might also find applications in construction, especially in areas requiring extreme durability.
HPQ silica sand can be considered environmentally friendly due to its natural origin. However, like any mining operation, responsible extraction and processing practices are essential to minimize environmental impact.
HPQ silica sand plays a role in renewable energy technologies like solar panels due to its high purity and thermal resistance. It enhances the efficiency and lifespan of these energy-generating systems.
HPQ silica is an essential component in the manufacturing of semiconductors and silicon wafers used in electronics. Its high purity ensures minimal impurities that could affect the performance of electronic devices.
The optical industry relies on HPQ silica for producing high-quality lenses, prisms, and other optical components. Its clarity, transparency, and thermal stability make it an ideal material for precision optical instruments.
HPQ silica is utilized in the production of ceramics and refractory materials due to its high temperature resistance and low thermal expansion. It’s often used in kiln furniture, crucibles, and insulating materials.
HPQ silica can be used to create thin films and coatings with specific properties, such as anti-reflective coatings for optical lenses, solar panels, and displays.
Silica fume, a byproduct of silicon metal production, is used as an additive in cement to improve its strength and durability. It reduces the permeability of concrete, making it more resistant to water and chemical penetration.
Silica nanoparticles are used in coatings and paints to improve their scratch resistance, UV protection, and moisture resistance. They can also provide a smooth finish and increase the longevity of painted surfaces.
Silica fillers are added to adhesives and sealants to improve their stability, adhesion, and resistance to environmental factors. They also enhance the thixotropic properties of these products.
Silica additives can enhance the properties of flooring materials, such as tiles and epoxy-based coatings. They contribute to abrasion resistance, surface hardness, and adhesion strength.